Anthropometrics in architectural design
Contents |
[edit] What is anthropometrics?
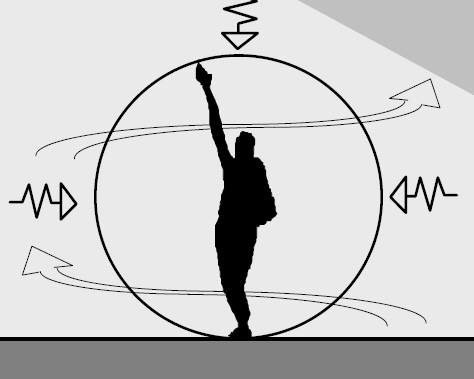
Anthropometrics is the comparative study of the measurements and capabilities of the human body. It derives from the Greek words 'anthropos' (meaning human), and 'metron' (meaning measure).
Anthropometry influences a wide range of industries, processes, services and products and has a considerable importance in optimising the design of buildings.
[edit] How does anthropometrics influence building design?
Human dimensions and capabilities are paramount in determining a building's dimensions and overall design. The underlying principle of anthropometrics is that building designs should adapt to suit the human body, rather than people having to adapt to suit the buildings.
There are two basic areas of anthropometry:
- Static anthropometry is the measurement of body sizes at rest and when using devices such as chairs, tables, beds, mobility devices, and so on.
- Functional anthropometry is the measurement of abilities related to the completion of tasks, such as reaching, manoeuvring and motion, and other aspects of space and equipment use.
The use of anthropometrics in building design aims to ensure that every person is as comfortable as possible. In practical terms, this means that the dimensions must be appropriate, ceilings high enough, doorways and hallways wide enough, and so on. In recent times, it has come to have particular significance for workplace design, and the relationship between desk, chair, keyboard and computer display.
Anthropometry may also impact on space requirements for furniture and fittings. For example, a bathroom must have enough space to comfortably fit a bath and sink; a bedroom must have enough space to comfortably fit an average-sized bed; an office building must have enough space to fit desks, air-conditioning units, communal areas, meeting rooms, and so on.
See also: Ergonomics.
[edit] Anthropometrics and inclusive design
The building regulations provide a range of standard requirements and approved solutions for designers to help develop suitable designs. However, it is important to consider the specific purpose and requirements of end users. Attempts to apply standardised dimensions may not reflect the true need of the space requirements.
Older people, children, people with mobility issues, wheelchair users and so on may have specific requirements. In particular, good accessibility and easy manoeuvrability around the building must be considered when designing stairs, lifts, ramps and other features. See Accessibility in the built environment for more information.
Anthropometric data is regularly updated to reflect changes in the population.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Accessibility in the built environment.
- Building spaces definition.
- Changing lifestyles.
- Concept architectural design checklist.
- Design intent.
- Design management for construction projects.
- Design responsibility matrix.
- Ergonomics in construction.
- Facilities management.
- Headroom.
- Inclusive design.
- Lifts.
- People with disabilities.
- Ramps.
- Scale.
- Skeuomorphism.
Featured articles and news
Microcosm of biodiversity in balconies and containers
How minor design adaptations for considerable biodiversity benefit.
CIOB student competitive construction challenge Ireland
Inspiring a new wave of Irish construction professionals.
Challenges of the net zero transition in Scotland
Skills shortage and ageing workforce hampering Scottish transition to net zero.
Private rental sector, living standards and fuel poverty
Report from the NRH in partnership with Impact on Urban Health.
.Cold chain condensing units market update
Tracking the evolution of commercial refrigeration unit markets.
Attending a conservation training course, personal account
The benefits of further learning for professsionals.
Restoring Alexander Pope's grotto
The only surviving part of his villa in Twickenham.
International Women's Day 8 March, 2025
Accelerating Action for For ALL Women and Girls: Rights. Equality. Empowerment.
Lack of construction careers advice threatens housing targets
CIOB warning on Government plans to accelerate housebuilding and development.
Shelter from the storm in Ukraine
Ukraine’s architects paving the path to recovery.
BSRIA market intelligence division key appointment
Lisa Wiltshire to lead rapidly growing Market Intelligence division.
A blueprint for construction’s sustainability efforts
Practical steps to achieve the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals.
Timber in Construction Roadmap
Ambitious plans from the Government to increase the use of timber in construction.
ECA digital series unveils road to net-zero.
Retrofit and Decarbonisation framework N9 launched
Aligned with LHCPG social value strategy and the Gold Standard.
Competence framework for sustainability
In the built environment launched by CIC and the Edge.
Institute of Roofing members welcomed into CIOB
IoR members transition to CIOB membership based on individual expertise and qualifications.
Join the Building Safety Linkedin group to stay up-to-date and join the debate.
Government responds to the final Grenfell Inquiry report
A with a brief summary with reactions to their response.


























Comments
[edit] To make a comment about this article, click 'Add a comment' above. Separate your comments from any existing comments by inserting a horizontal line.